- Introduction: Why Teach Robots the Art of Manzai Comedy?
- What the Patent Drawing Reveals About the Gesture-Capable Robot
- How the Manzai Performance Mechanism Works
- Benefits for Entertainment, Education, and Robotics
- Engineering Considerations
- Patent Attorney’s Thoughts
- Application of the Technology: “Expressive Performance Robotics Platform”
- Final Reflections
Introduction: Why Teach Robots the Art of Manzai Comedy?
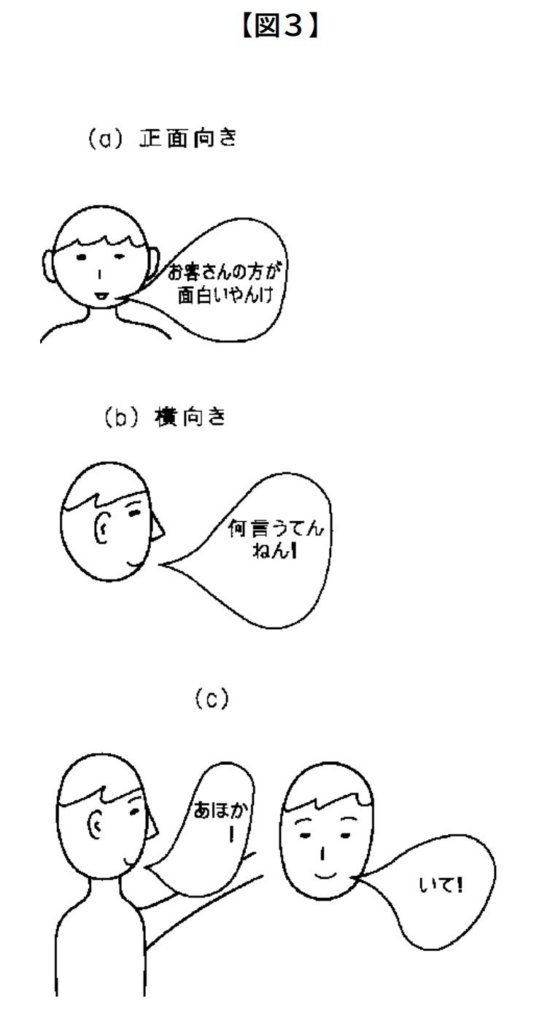
Manzai—the fast-paced, two-person Japanese comedy style—relies on timing, rhythm, body language, and sharp contrast between the “straight man” and the “funny man.” This patent drawing presents a robot engineered to perform manzai routines with expressive gestures, translating comedic performance into mechanical motion. It merges cultural expression with robotics, turning humor into programmable movement.
What the Patent Drawing Reveals About the Gesture-Capable Robot
The illustration highlights a humanoid robot designed for comedic delivery:
- Articulated arms capable of broad or rapid gestures
- Torso joints allowing bowing, leaning, and reaction movements
- Head motion synchronized with dialogue timing
- Gesture modules linked to speech or script progression
- A stable base preventing tipping during energetic performance
The physical design supports exaggerated comedic motion.
How the Manzai Performance Mechanism Works
The mechanism allows synchronized humor through:
- A script engine that manages manzai timing
- Motion controllers linked to comedic beats
- Pre-programmed reaction gestures—surprise, frustration, emphasis
- Coordinated arm swings and head movement
- Safety controls during high-energy gestures
The robot essentially “performs” its role as if on a real comedy stage.
Benefits for Entertainment, Education, and Robotics
- Introduces Japanese comedy culture in interactive form
- Useful for theme parks, stage shows, or exhibitions
- An engaging teaching tool for language rhythm and humor
- Demonstrates advanced motion-synchronization technology
- Serves as a platform for robot personality research
It blends cultural storytelling with engineering innovation.
Engineering Considerations
Key technical points include:
- Actuator durability under rapid repetitive movement
- Gesture accuracy and synchronized timing
- Preventing overextension during wide arm swings
- Maintaining center of gravity in comedic “overreactions”
- Noise reduction for enjoyable audience experience
Robotics must accommodate the rhythm of humor.
Patent Attorney’s Thoughts
Comedy is timing—and timing is engineering.
By giving a robot gestures that rise, fall, hesitate, and explode, this invention shows how machines may someday share a stage with human performers in ways both surprising and delightful.
Application of the Technology: “Expressive Performance Robotics Platform”
Purpose
To enable robots to execute manzai-style comedic gestures synchronized with dialogue.
System Components
- Script timing engine
- Gesture control actuators
- Humanoid arm and torso joints
- Head-movement synchronizer
- Stabilized performance base
Operational Flow
- Load comedic script into timing engine.
- Execute gestures based on cues.
- Synchronize head and arm movements with dialogue.
- React with pre-programmed emotional gestures.
- Maintain balance during dynamic motion.
Final Reflections
This invention expands robots beyond utility—giving them rhythm, performance, and humor that bridge culture and technology.
Disclaimer: This content is an AI-generated reinterpretation based on a patent drawing.
It is provided for educational and cultural purposes only, and not as legal advice.
↓Related drawing↓