- Introduction: Why Study the Layered Structure of 3D-Printed Sushi?
- What the Patent Drawing Reveals About the Layer Geometry
- How the 3D-Printed Layering Mechanism Works
- Benefits of Digitally Layered Food Construction
- Engineering Considerations
- Patent Attorney’s Thoughts
- Application of the Technology: “Digital Sushi Layer-Modeling Platform”
- Final Reflections
Introduction: Why Study the Layered Structure of 3D-Printed Sushi?
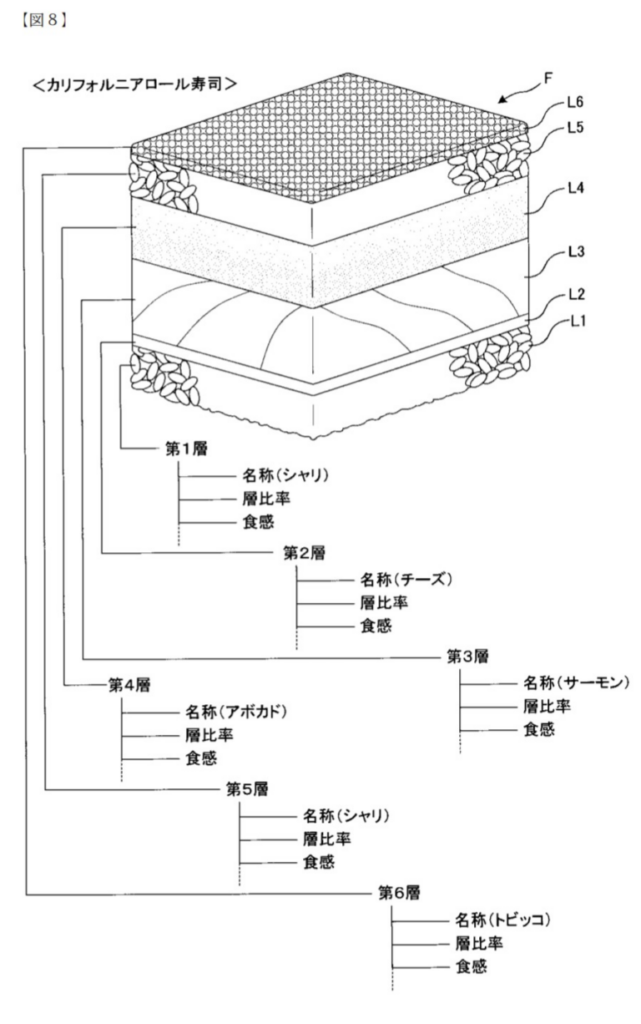
The idea of 3D-printed sushi brings together culinary tradition and digital fabrication. A California roll may look simple, but reproducing its layered structure through additive manufacturing requires precise modeling of textures, densities, and ingredient placement. This patent drawing reveals how sushi can be represented as a layered, printable structure, enabling food customization, automated production, and artistic food expression.
What the Patent Drawing Reveals About the Layer Geometry
The drawing shows a multi-layered cylindrical construction featuring:
- An outer sheet representing seaweed (nori)
- A rice layer modeled with controlled thickness
- A central core containing ingredients such as avocado, crab, or cucumber
- A structural segmentation method defining printable boundaries
- A cross-section designed for accurate texture mapping
The design treats sushi as a structured food object suitable for 3D output.
How the 3D-Printed Layering Mechanism Works
The mechanism converts culinary components into printable elements:
- Each ingredient is represented as a digital layer
- The printer extrudes food material in concentric or segmented paths
- Thickness and density are controlled to replicate bite texture
- The core ingredients are deposited before the outer layers seal the structure
- The result forms a stable, edible, multilayer roll
It blends gastronomy with computational modeling.
Benefits of Digitally Layered Food Construction
- Enables customized shapes, fillings, and nutrition profiles
- Offers consistent quality in commercial food production
- Supports creative culinary design for restaurants or events
- Promotes efficient automated assembly
- Useful for education, food R&D, or accessibility-focused meal preparation
It turns sushi into a programmable food geometry.
Engineering Considerations
Creating 3D-printed food requires attention to:
- Material viscosity and extrusion behavior
- Temperature control for ingredients
- Accurate deposition of soft components like rice
- Structurally sound inner cores
- Food-safe printing pathways and hygiene considerations
Digital food must satisfy engineering and culinary requirements.
Patent Attorney’s Thoughts
There is poetry in translating cuisine into geometry.
A California roll becomes a set of layers—simple, ordered, and yet full of texture.
This drawing shows how technology can reinterpret tradition, preserving its essence while exploring new forms of creation.
Application of the Technology: “Digital Sushi Layer-Modeling Platform”
Purpose
To digitally model layered sushi structures for precise, automated 3D-printed food creation.
System Components
- Ingredient-based digital layers
- Multi-material food extruders
- Concentric or segmented printing paths
- Density-control algorithms
- Food-safe build platform
Operational Flow
- Sushi layers are digitally mapped.
- The printer extrudes inner ingredients.
- Rice layers are added with controlled density.
- Nori or outer layer seals the structure.
- The roll is completed as a stable, printed food item.
Final Reflections
This invention shows how tradition can be transformed through precision—building flavor as geometry, and food as design.
Disclaimer: This content is an AI-generated reinterpretation based on a patent drawing.
It is provided for educational and cultural purposes only, and not as legal advice.
↓Related drawing↓